PLC splitter is an important fiber optic products in passive fiber optic networks. As you may thought that how to divide fiber optic signals to different users? Then PLC splitter is a best solution for that. To make it fit different environments or application, PLC splitters are often designed in different types. This post would give you a general knowledge for understanding plc splitters if you are a buyer or seller for fiber optics.
What is a PLC Splitter?
PLC stands for Planar Lightwave Circuit. A PLC splitter is a type of optical power management device that is used to distribute or combine optical signals. It is constructed using silica optical waveguide technology to distribute light from a single input into multiple output fibers uniformly, ensuring minimal variation in intensity.
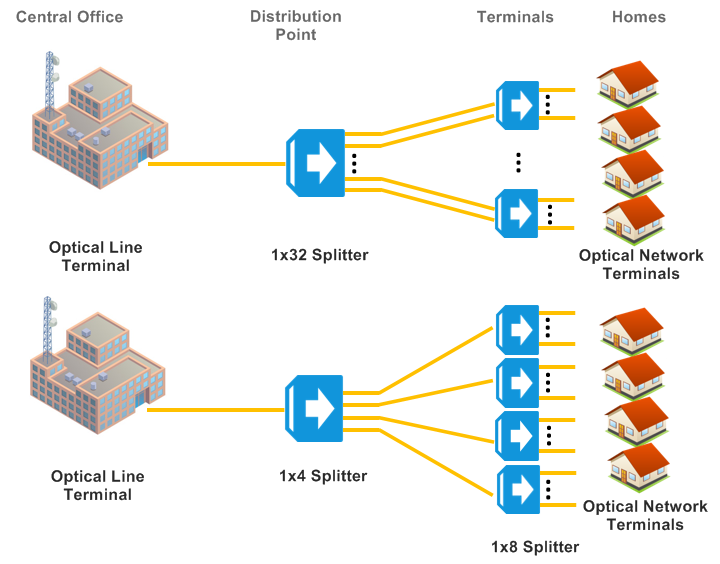
How PLC Splitter Works?
The core principle behind a PLC splitter is based on the waveguide properties of light. It utilizes optical waveguides etched onto a silica glass substrate to split the light. The input light is introduced into the device, which then gets evenly distributed among the output ports through the waveguide paths. This process occurs with minimal loss, high consistency, and uniformity, making PLC splitters highly reliable and efficient for splitting light.
Types of PLC Splitters
PLC splitters can be categorized based on their output configurations and packaging types:
- Based on Output Configurations:
- 1xN Splitters: These splitters divide the light from one input fiber into multiple outputs (N), e.g., 1×8, 1×16, 1×32, etc.
- 2xN Splitters: These are similar to 1xN splitters but have two input fibers, allowing for more complex splitting configurations, e.g., 2×8, 2×16, 2×32, etc.
- Based on Packaging Types:
- Bare Fiber Type: The splitter has no outer casing, making it suitable for integration into other equipment.
- Blockless Fiber Type: Compact design, typically used in small spaces like splice trays.
- ABS Box Type: Encased in an ABS plastic box, providing protection and durability.
- LGX Box and Rack Mount: Suitable for easy integration into standard networking equipment and racks.

Key Parameters in PLC Splitters
When selecting a PLC splitter, consider the following parameters:
- Insertion Loss (IL): The loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of the device in the optical fiber, measured in dB. Lower is better.
- Uniformity: The variation in insertion loss between the different output ports. Excellent uniformity means minimal variation.
- PDL (Polarization Dependent Loss): The difference in insertion loss as the light’s polarization state changes. Lower PDL indicates better performance.
- Return Loss (RL): The amount of light reflected back to the source, measured in dB. Higher return loss values are preferable.
- Operating Wavelength: The range of wavelengths the splitter can operate within, typically around 1260nm to 1650nm for most applications.
PLC Splitter Parameters:
| Input x Output Port Number | 1×2 | 1×4 | 1×8 | 1×16 | 1×32 | 1×64 | ||
| Optical Fiber Diameter | um | 9/125 | ||||||
| Operating Wavelength | nm | 1260- 1650 | ||||||
| Insertion Loss (include PDL) | Typical | B | ≤ 3.6 | ≤7.0 | ≤ 10.3 | ≤ 13.6 | ≤ 16.6 | ≤20.1 |
| Max | B | 4 | 7.1 | 10.5 | 13.7 | 16.9 | 21 | |
| Uniformity’ Max | B | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | |
| PDL Max | B | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |
| Return Loss | B | ≥50 | ≥50 | ≥50 | >50 | ≥50 | ≥50 | |
| Directivity’ | B | ≥ 55 | ≥ 55 | ≥ 55 | ≥ 55 | ≥ 55 | ≥ 55 | |
| Output Fiber Type | 4-fiberribbonx1 | 4-fiber ribbonx2 | 8-fiber ribbonx2 | 8-fiber ribbonx4 | 8-fiberribbonx8 | |||
| Case Size (For bare Fiber) | mm | 40(L)x4(W)x4(H) | 50(L)x7(W)x4(H) | 60()x12M) x4(H) | ||||
| Case Size* (For 0.9 LooseTube) | mm | 60(L)x7(W)x4(H | 60(L)x20(W)x4(H) | 80(L)x20 (W) x6(H) | 100(L)x40(W)x6(H) | |||
| Operation Temperature | ℃ | -40~ 85 | ||||||
| Characteristics Are Characteristics without connectors under room temperature at 1310nn/1550 nm | ||||||||
How to Use a PLC Splitters?
PLC splitters are widely used in PON (Passive Optical Network) networks, connecting the central office and the end users in FTTH (Fiber to the Home) deployments. To use a PLC splitter, simply integrate it into the optical network where signal distribution is required. It’s crucial to ensure compatibility with the network’s wavelength and the physical installation space.
How to Choose PLC Splitters?
Choosing the right PLC splitter involves:
- Choose 1xN or 2XN PLC Splitter: Determine the split ratio needed and the number of end users. N stands for the end users number.
- Considering types of PLC Splitter to suit to the Operating Environment: Select the packaging type based on the installation environment (indoor, outdoor, space constraints). such as bare fiber, blockless type, ABS box type, LGX type etc.
- Evaluating PLC Splitter Technical Parameters: Ensure the splitter’s specifications (IL, RL, PDL, uniformity) meet or exceed your network’s performance criteria. Most of time the standard parameters are enough for telecom providers.
- Budgeting: While not compromising on quality, consider cost-effective options that offer the necessary performance characteristics. Here in Bativ, you will have competitive prices to wholesale PLC splitters from us.
- Special requirements: If you are looking for 1×6, 1×12, 1×24 plc splitter or multimode plc fiber splitters, You can contact our sales expert directly for instant support.
Conclusion
PLC splitters are indispensable in the realm of optical networking, offering a highly reliable and efficient method of distributing light signals. Understanding their principles, types, and operational parameters helps in selecting the right splitter for your network’s needs. Whether you’re designing a new network or upgrading an existing one, a properly chosen PLC splitter can significantly enhance performance and reliability.
If you are looking for a plc splitter supplier, Bativ will be one of the right suppliers to make your purchasing easy and cost-effective.